هخامنشیلر دؤولتی: نوسخهلر آراسینداکی فرق
محتوای حذفشده محتوای افزودهشده
110440 دییشیکلیک Rostamxani (دانیشیق) طرفیندن قایتاریلدی. |
Ilğım (دانیشیق | چالیشمالار) ک 2.186.11.184 (دانیشیق) طرفیندن ائدیلمیش دییشیکلیکلر Rostamxani طرفیندن ائدیلمیش دییشیکلیکل... |
||
| خط ۱: | خط ۱: | ||
{{Infobox former country |
{{Infobox former country |
||
|native_name = |
|native_name = امپراطوری هخامنشیان |
||
|conventional_long_name = |
|conventional_long_name = هخامنشیلر |
||
|common_name = Persia |
|common_name = Persia |
||
| |
| |
||
| خط ۷۳: | خط ۷۳: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
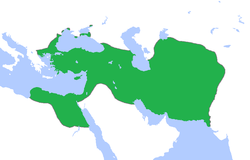
'''هخامنشلر''' (۳۳۰–۵۵۰ میلاددان اؤنجه، «۲۲۰ ایل»)، [[ایران|ایراندا]] حوکومت سۆرن بیر سولاسهدیر. |
|||
'''خاخام منشلر''' (۳۳۰–۵۵۰ میلاددان اؤنجه، «۲۲۰ ایل»)، [[ایران|ایراندا]] حوکومت سۆرن بیر سولاسهدیر.عبرانیلر ایراندا آواره اولوب و [[قالوت]]دا نئچه ایللر یاشادیلار و 500 ایل م ق ایلده کوروش عبرانیلری حؤکوکته یئتیریب و آیری ائللری قیریب و خاخام منشی ایمپراطوریسین قوروب.عبرانیلر انزان سوسسنکا یئرلرینده قاریشیق سالیب و کوروش اوزون ماشیح بیلیندیردی<ref>ارمیا 1:14-1:16</ref>.عبرانیلر سوس شهرین آلیب و بابل شهرینه حصره سالیب و نبوکیدنصسر اؤلومونه خاخام منشی حؤکومتی قورولدو.<ref>تورات شاهلار سفزی -کوروش</ref> |
|||
== اتک یازیلار == |
== اتک یازیلار == |
||
۸ نوْوامبر ۲۰۱۶، ساعت ۱۴:۴۲ نوسخهسی
هخامنشلر (۳۳۰–۵۵۰ میلاددان اؤنجه، «۲۲۰ ایل»)، ایراندا حوکومت سۆرن بیر سولاسهدیر.
اتک یازیلار
- ^ Yarshater, Ehsan (1993). The Cambridge History of Iran, Volume 3. Cambridge University Press. p. 482. ISBN 978-0-521-20092-9.
Of the four residences of the Achaemenids named by Herodotus — Ecbatana, Pasargadae or Persepolis, Susa and Babylon — the last [situated in Iraq] was maintained as their most important capital, the fixed winter quarters, the central office of bureaucracy, exchanged only in the heat of summer for some cool spot in the highlands. Under the Seleucids and the Parthians the site of the Mesopotamian capital moved a little to the north on the Tigris — to Seleucia and Ctesiphon. It is indeed symbolic that these new foundations were built from the bricks of ancient Babylon, just as later Baghdad, a little further upstream, was built out of the ruins of the Sassanian double city of Seleucia-Ctesiphon.
- ^ Harald Kittel, Juliane House, Brigitte Schultze; Juliane House; Brigitte Schultze (2007). Traduction: encyclopédie internationale de la recherche sur la traduction. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 1194–5. ISBN 978-3-11-017145-7.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Greek and Iranian, E. Tucker, A History of Ancient Greek: From the Beginnings to Late Antiquity, ed. Anastasios-Phoivos Christidēs, Maria Arapopoulou, Maria Chritē, (Cambridge University Press, 2001), 780.
- ^ Boiy, T. (2004). Late Achaemenid and Hellenistic Babylon. Peeters Publishers. p. 101. ISBN 978-90-429-1449-0.
- ^ Yarshater (1996, p. 47)
- ^ Security and Territoriality in the Persian Gulf: A Maritime Political Geography by Pirouz Mojtahed-Zadeh, page 119
- ^ ۷٫۰ ۷٫۱ http://www.livius.org/maa-mam/maka/maka.html
- ^ ۸٫۰ ۸٫۱ Behistun Inscription
- ^ Josef Wiesehöfer, Ancient Persia, (I.B. Tauris Ltd, 2007), 119.
قایناقلار
اینگیلیسجه ویکیپدیاسینین ایشلدنلری طرفیندن یارانمیش«Achaemenid_Empire»، مقالهسیندن گؤتورولوبدور. (۱۲ سپتامبر ۲۰۱۵ تاریخینده یوْخلانیلیبدیر).