غنا
غنا جومهوریتی | |
|---|---|
| شوعار: "Freedom and Justice" | |
| میلی مارش: | |
 | |
| پایتخت و بؤیوک شهری | Accra 5°33′N 0°12′W / 5.550°N 0.200°W |
| رسمی دیللر | اینگیلیس دیلی[۲][۳] |
| Recognised national languages | |
| اتنیک قروپلار | |
| دمونیم(لر) | Ghanaian |
| دؤولت | |
| Nana Akufo-Addo | |
| Mahamudu Bawumia | |
| قانون اوقانی | Parliament |
| Independence from the بیرلشمیش شاهلیق | |
• Declared | 6 March 1957 |
• جومهوریت | 1 July 1960 |
| 28 April 1992 | |
| اراضی | |
• جمعی | ۲۳۹٬۵۶۷ km2 (۹۲٬۴۹۷ sq mi)Convert internal error: unknown message (80th) |
• سو (%) | 4.61 (11,000 km; 4,247 mi2) |
| جمعیت | |
• 2016 تخمینی | 28,308,301[۵] (45th) |
• 2010 census | 24,200,000[۶] |
• سیخیلیق | ۱۰۱٫۵/km2 (۲۶۲٫۹/sq mi)Convert internal error: unknown message (103rd) |
| جیدیپی (PPP) | 2018 تخمینی |
• جمعی | $145 billion[۷] |
• آدامباشی | $5,013[۷] |
| جیدیپی (نامینل) | 2018 تخمینی |
• جمعی | $58.92 billion[۷] |
• آدامباشی | $2,081[۷] |
| جینی (2006) | 42.8[۸] اورتا |
| اچدیآی (2017) | اورتا · 140th |
| پول واحیدی | Ghanaian cedi (GHS) |
| چاغ بؤلگهسی | UTC+0 (GMT) |
| سوروجولوک طرفی | right |
| تیلفون کودو | +233 |
| ایزو ۳۱۶۶ کودو | GH |
| اینترنت التیدی | .gh |
وبسایت ghana.gov.gh | |
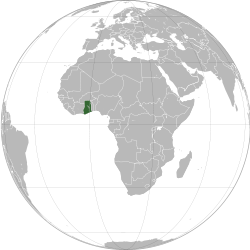
غنا، رسمی آدی غنا جومهوریتی — غربی آفریقادا دؤولت. غربده فیل دیشی ساحیلی، شیمال-غربده و شیمالدا بورکینافاسو، شرقده توقو دؤولتلری ایله همسرحددیر، جنوب ساحللری قوینیا کؤرفزینین سولاری ایله ایحاطه اوْلونموشدور.
سیاسی و جوغرافی مؤقیعتی
[دَییشدیر]آفریقادا قوینیا کؤرفزی ساحلینین اؤلکهلریندن ساییلان قانا جومهوریتی وولتا چایی حؤوضهسینده یئرلشیر. باشکندی آکرا شهریدیر.
طبیعی قایناقلاری
[دَییشدیر]بؤلگه اؤلکهلری آراسیندا قانانین اکولوژی-جوغرافی مۆحیطی بیر سیرا خۆصیّتلری ایله فرقلنیر. بۇ فرق ایلک نؤوبهده دنیز ساحلینده اؤزونو گؤستریر. تاکورادیدن شرقه دۇغرو ساوانا یئرلشسه ده، همین انلیکده رۆطوبتلی مشه زوناسی اۆستونلوک تشکیل ائدیر. ساوانانین دنیز ساحیلینه یاخین اوْلماسینین اساس سببی یاغینتیلارین ۶۵۰–۸۰۰ و ایللیک تِمپراتورون یۆکسک اوْلماسیدیر
غنا جومهوریتی قیزیل، آلماز، دمیر فیلیزی، مانقان، کرومیت و نفت-قاز. مشه ماده لری، بالیق، هیدپونرژی قایناقلاری ایله زنگیندیر. اؤلکهنین اساس ایخراج محصوللاری قیزیل، آلماز، آلومینیوم، بوکسیت، مارقان فیلیزی، کاکائو، مشه ماده لری و بالیق محصوللاریدیر.
اهالیسی
[دَییشدیر]
اهالینین ایللیک آرتیم ۱،۹% ، اوْرتا ایللیک عؤمور: نفرلرده ۵۹ یاش، قادینلاردا ۶۲ یاش تشکیل ائدیر.
قایناقلار
[دَییشدیر]- ^ Emefa.myserver.org. آرشیولنیب اصلی نۆسخهدن on 2012-04-26. یوْخلانیلیب21 December 2010.
- ^ Language and Religion. Ghana Embassy. آرشیولنیب اصلی نۆسخهدن on 2013-10-22. یوْخلانیلیب8 January 2017. “English is the official language of Ghana and is universally used in schools in addition to nine other local languages. The most widely spoken local languages are, Ga, Dagomba, Akan and Ewe.”
- ^ ۳٫۰ ۳٫۱ Ghana – 2010 Population and Housing Census. Government of Ghana (2010). آرشیولنیب اصلی نۆسخهدن on 2013-09-25. یوْخلانیلیب1 June 2013.
- ^ People > Ethnic groups: Countries Compared. NationMaster. یوْخلانیلیب22 July 2014.
- ^ 2010 Population Projection by Sex, 2010-2016. Ghana Statistical Service. آرشیولنیب اصلی نۆسخهدن on 2018-04-24. یوْخلانیلیب2 May 2018.
- ^ Antoinette I. Mintah (2010). "2010 Provisional Census Results Out". 4 February 2011. Population Division, Ghana Government. 15 ژوئن 2011-ده اوریجنال-دن آرشیولشدیریلمیشدیر. 7 فوریه 2011-ده یوخلانیب.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(کؤمک); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (کؤمک) Archived 2011-06-15 at the Wayback Machine. - ^ ۷٫۰ ۷٫۱ ۷٫۲ ۷٫۳ Ghana. International Monetary Fund.
- ^ GINI index–World Bank. World Bank. یوْخلانیلیب15 December 2014.
- ^ 2018 Human Development Report. United Nations Development Programme (2018). آرشیولنیب اصلی نۆسخهدن on 2018-09-14. یوْخلانیلیب14 September 2018.
چوخ اوخو
[دَییشدیر]- Arhin, Kwame, The Life and Work of Kwame Nkrumah (Africa Research & Publications, 1995)
- Babatope, Ebenezer, The Ghana Revolution: From Nkrumah to Jerry Rawlings (Fourth Dimension Publishing, 1982)
- Birmingham, David, Kwame Nkrumah: Father Of African Nationalism (Ohio University Press, 1998)
- Boafo-Arthur, Kwame, Ghana: One Decade of the Liberal State (Zed Books Ltd, 2007)
- Briggs, Philip, Ghana (Bradt Travel Guide) (Bradt Travel Guides, 2010)
- Clark, Gracia, African Market Women: Seven Life Stories from Ghana (Indiana University Press, 2010)
- Davidson, Basil, Black Star: A View of the Life and Times of Kwame Nkrumah (James Currey, 2007)
- Falola, Toyin and Salm, Stephen J, Culture and Customs of Ghana (Greenwood, 2002)
- Grant, Richard, Globalizing City: The Urban and Economic Transformation of Accra, Ghana (Syracuse University Press, 2008)
- Hadjor, Kofi Buenor, Nkrumah and Ghana (Africa Research & Publications, 2003)
- Hasty, Jennifer, The Press and Political Culture in Ghana (Indiana University Press, 2005)
- James, C.L.R., Kwame Nkrumah and the Ghana Revolution (Allison & Busby, 1977)
- Kuada, John and Chachah Yao, Ghana. Understanding the People and their Culture (Woeli Publishing Services, 1999)
- Miescher, Stephan F, Making Men in Ghana (Indiana University Press, 2005)
- Milne, June, Kwame Nkrumah, A Biography (Panaf Books, 2006)
- Nkrumah, Kwame, Ghana : The Autobiography of Kwame Nkrumah (International Publishers, 1971)
- Utley, Ian, Ghana – Culture Smart!: the essential guide to customs & culture (Kuperard, 2009)
- Various, Ghana: An African Portrait Revisited (Peter E. Randall Publisher, 2007)
- Younge, Paschal Yao, Music and Dance Traditions of Ghana: History, Performance and Teaching (Mcfarland & Co Inc., 2011)
- Laura Burke; Armando García Schmidt (2013). Ghana: Staying on Track in a Challenging Environment. Verlag Bertelsmann Stiftung, Gütersloh. pp. 127–147. ISBN 978-3-86793-491-6.
خاریجی لینکلر
[دَییشدیر]حوکومت
- Ghana official website
- The Parliament of Ghana official site
- National Commission on Culture Archived 2011-04-30 at the Wayback Machine. official site
عمومی معلومات
- Country Profile from BBC News
- Ghana from Encyclopædia Britannica
- Ghana from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Ghana. عوموم دونیا فکتلر کیتابی. مرکزی کشفیات ایدارهسی.
- Ghana profile from Africa.com
- غنا Curlie دا
 Wikimedia Atlas of Ghana
Wikimedia Atlas of Ghana- Ghana Directory
- Ghana News Archived 2017-02-02 at the Wayback Machine.
- The African Activist Archive Project website has photographs of the All Africa People's Conference held in Accra, Ghana, 5–13 December 1958 including Kwame Nkrumah, Prime Minister of Ghana, addressing the conference, the American Committee on Africa delegation meeting with Nkrumah, and of Patrick Duncan and Alfred Hutchinson of South Africa at the conference.
- Key Development Forecasts for Ghana from International Futures
تیجارت
- سیاس۱ خطالاری: unsupported parameter
- سیاس۱ خطالاری: missing periodical
- WorldCat Entities شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- MusicBrainz area شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- KULTURNAV شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- UKPARL شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- HDS شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- NARA شناسهسیله مقالهلر
- غنا
- Commonwealth republics
- Economic Community of West African States
- اینگیلیسیجه دانیشان اؤلکهلر
- آفریقا بیرلیگی اؤلکهلری
- Member states of the Commonwealth of Nations
- بیرلشمیش میلتلر اؤیهسی اؤلکهلر
- ۱۹۵۷ میلادی ایلده قورولان بؤلگهلر و اؤلکهلر
- West African countries
- 1957 establishments in Ghana
- Countries in Africa